MacOS 10.12 Sierra¶
According to Wikipedia Sierra is “(version 10.12) is the thirteenth major release of macOS (previously OS X), Apple Inc.’s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. The successor to OS X El Capitan, it is the first version of the operating system issued under the June 2016 rebranding as macOS. Sierra is named after California’s Sierra Nevada mountain range. Its major new features concern Continuity, iCloud, and windowing, as well as support for Apple Pay and Siri.”.
- Applications
- Allow only signed apps
- Check Privacy permissions
- Destroy FileVault Keys
- Disable Creation of Metadata Files
- Disable Diagnostics
- Disable Guest user
- Disable Handoff
- Disable password hints
- Disable recent items
- Disable Localization Services
- Disable Spotlight Suggestions
- Enable FileVault
- Enable Firewall
- Enable screen saver
- Empty trash securely
- Erase free space
- Homebrew hardening
- Power off memory during standy
- Require an administration password
- Require password to un-lock
- Save to Disk by Default
- Set a Firmware Password
- Show all filename extensions
- Show when localization is used
- Users privilege separation
- References
Applications¶
It is suggested to keep the /Applications/ directory as clean as possible, having a separate Applications directory for your apps. Just create a folder named “Applications” in your home directory (or where you like) and install (move) all applications there. Apps installed via App Store or some special apps cannot live in a custom Applications folder, so you have to keep them in the original Applications.
Allow only signed apps¶
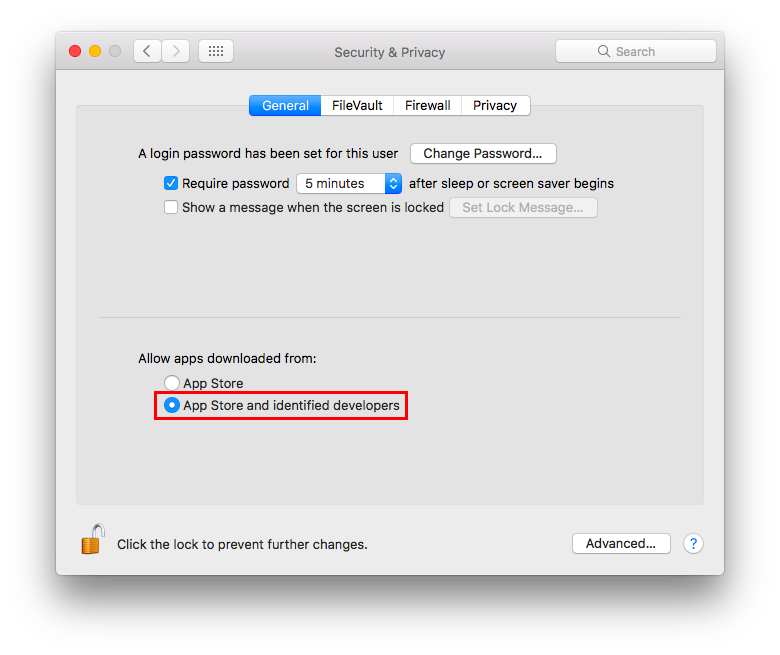
It is suggested to never run untrusted code not signed with a proper key. To allow only apps signed by an authorized developer, go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ General
Set “Allow apps download from” to “Mac App Store and identified developers” or if you want to be more strict and you install applications only via App Store set it to “Mac App Store”. In OS X Sierra is now not possible to choose to run unsigned code, it was in OS X El Capitan.
Check Privacy permissions¶
OS X allows you to track all applications requesting access to some sort of sensitive data, for example your location or your contacts. It is suggested to periodically check the list of applications requesting access to sensitive data and review their permissions. To show the list of these applications go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ Privacy

Destroy FileVault Keys¶
By default File Vault keys are kept when system goes in standby mode. As suggested by man pmset:
- destroyfvkeyonstandby - Destroy File Vault Key when going to standby
- mode. By default File vault keys are retained even when system goes to standby. If the keys are destroyed, user will be prompted to enter the password while coming out of standby mode.(value: 1 - Destroy, 0 - Retain)
It is suggested to configure your system to destroy File Vault keys when enterging in standy mode with the following command:
sudo pmset destroyfvkeyonstandby 1
Disable Creation of Metadata Files¶
By default OS X creates metadata files in each directory to speed up browsing. These files could leak metadata, it is suggested to avoid creation of .DS_Store and AppleDouble files.
Disable Creation of Metadata Files on Network Volumes with the following command in a Terminal:
defaults write com.apple.desktopservices DSDontWriteNetworkStores -bool true
Disable Creation of Metadata Files on USB Volumes with the following command in a Terminal:
defaults write com.apple.desktopservices DSDontWriteUSBStores -bool true
Disable Diagnostics¶
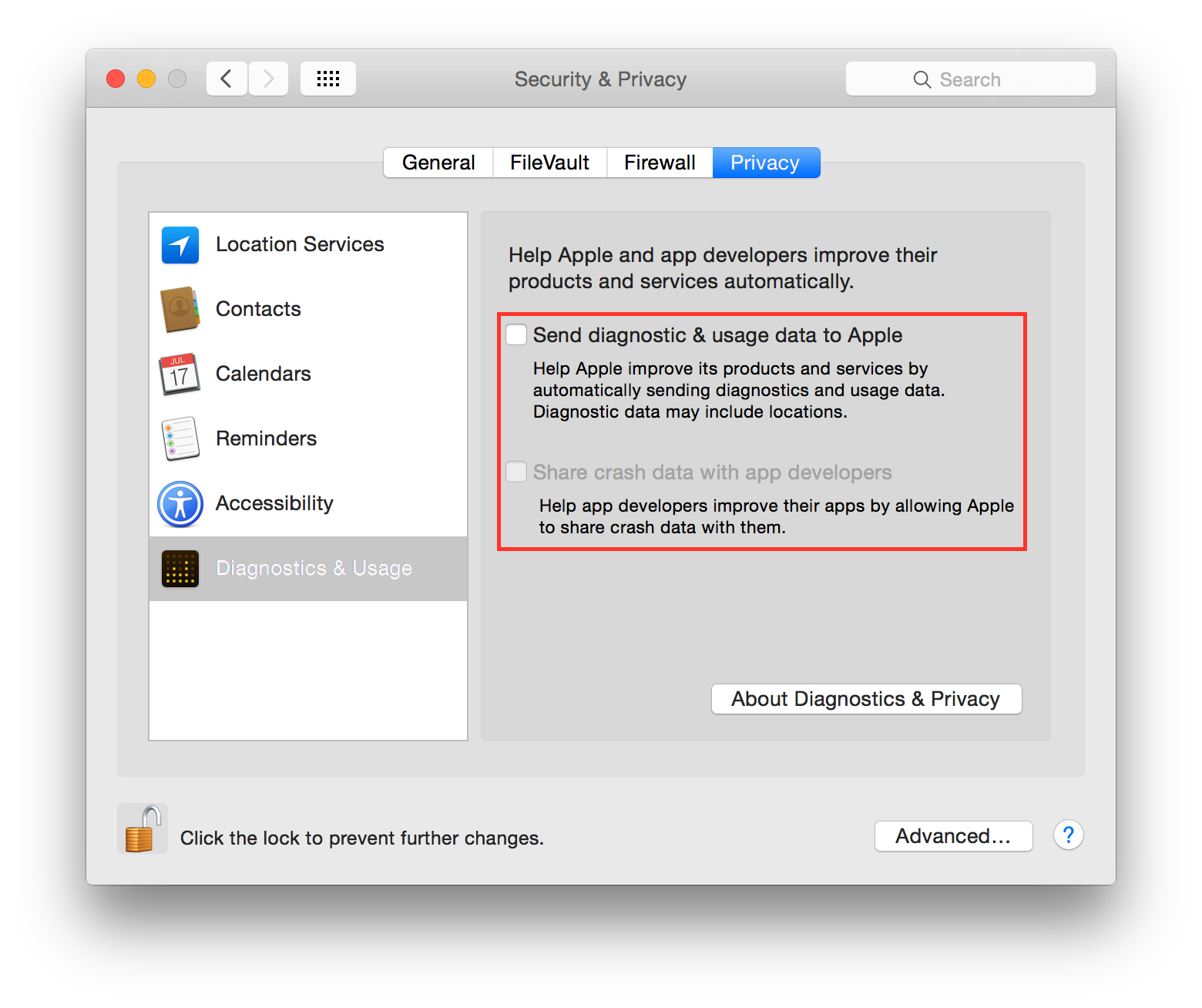
It is suggested to disable diagnostic data and usage data to Apple. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ Privacy ⇒ Diagnostics & Usage
Un-check “Send diagnostic & usage data to Apple”. Un-check “Share crash data with app developers”.
Disable Guest user¶
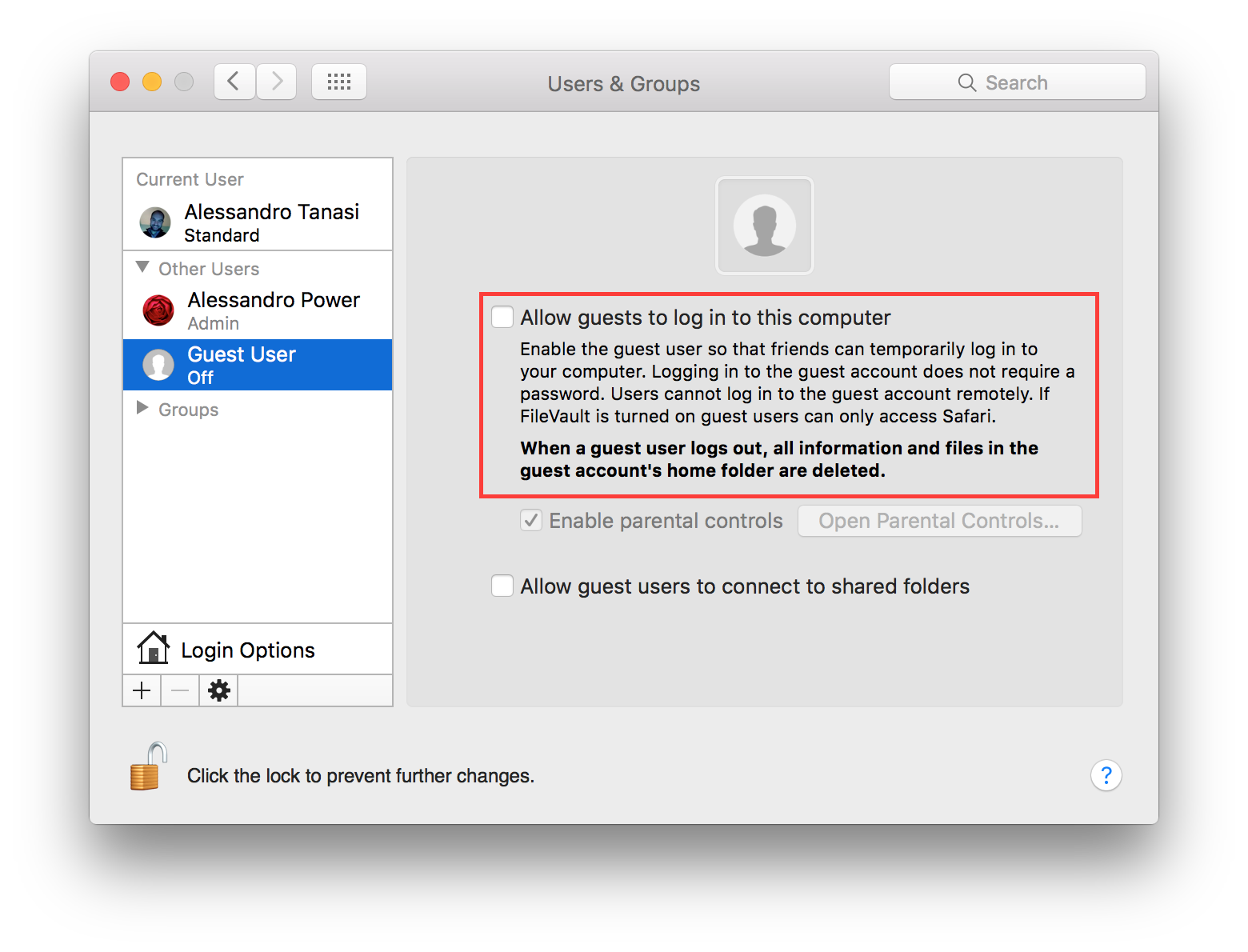
Mac OS X comes with a Guest user enabled by default, it permits the use of your device in a restricted environment to anyone. It is suggested to disable the Guest user, go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Users & Groups ⇒ Guest User
Un-check “Allow guests to log in to this computer”.
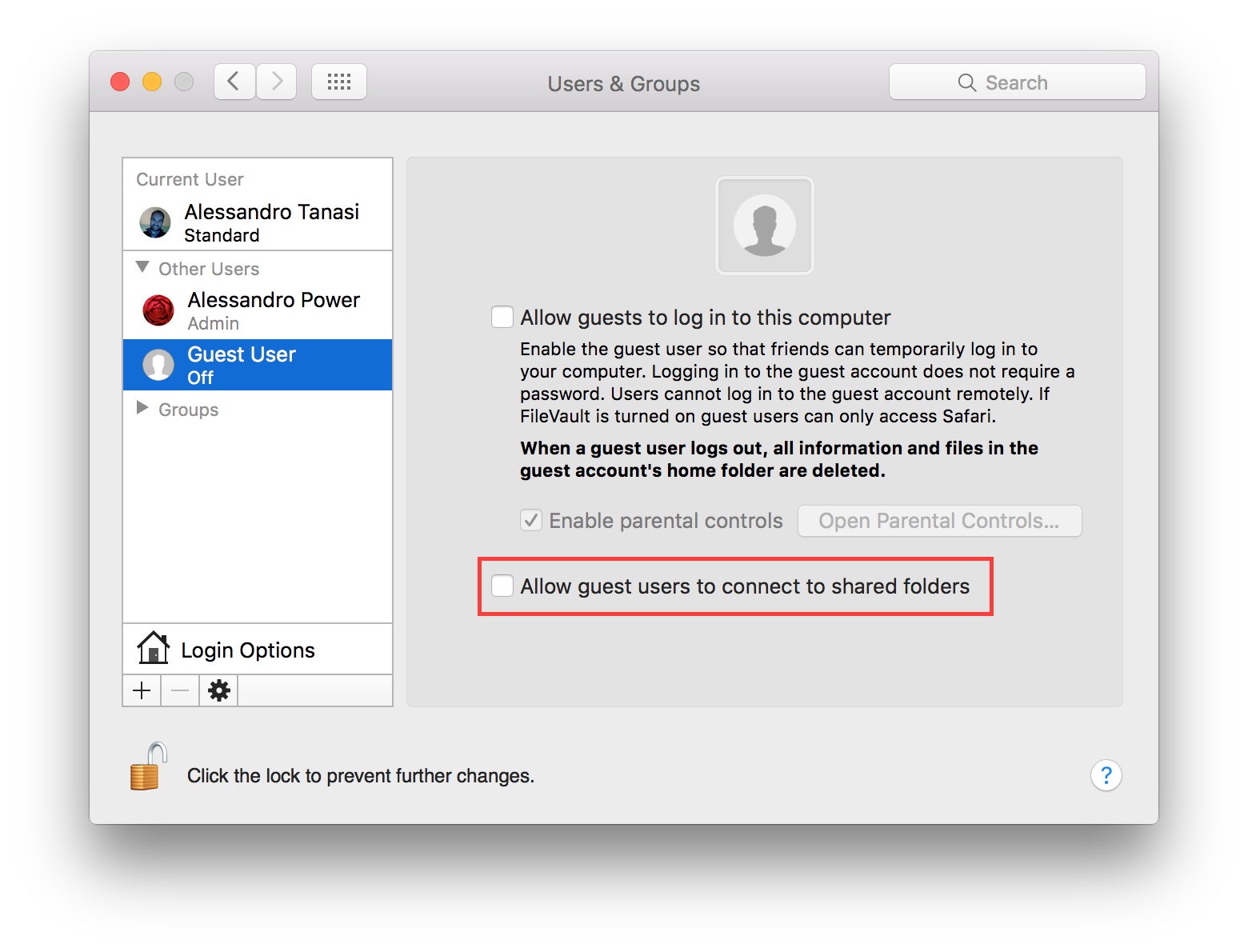
It is suggested to disable guest access to shared folders, if you are not using it, go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Users & Groups ⇒ Guest User
Un-check “Allow guest users to connect to shared folders”.
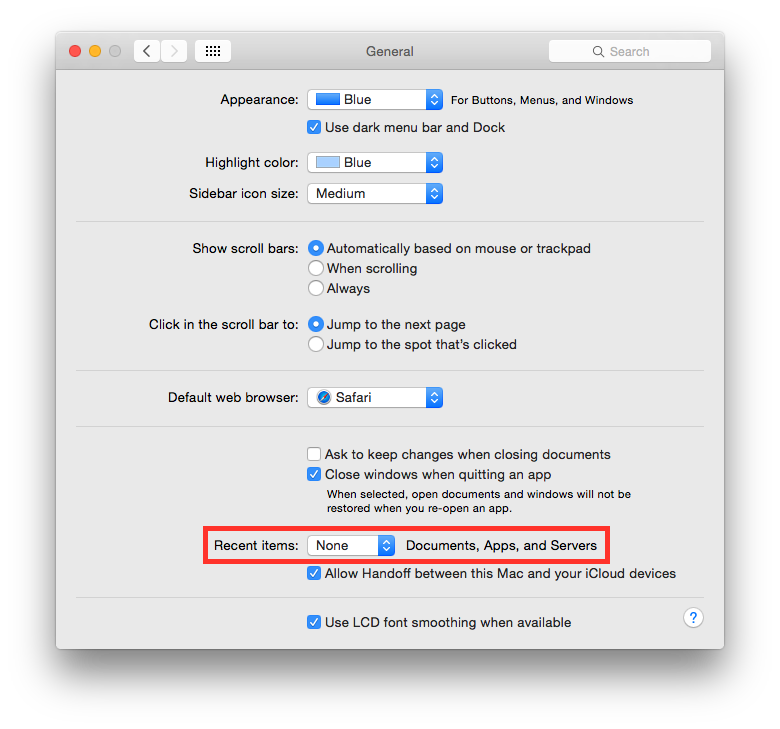
Disable Handoff¶
Handoff is a great feature to keep your work in sync between Apple devices. Due to his implementation it needs to send some data to Apple iCloud to work, so in some way it is leaking your data. It is suggested to disable it. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ General
Un-check “Allow Handoff between this Mac and your iCloud devices”.
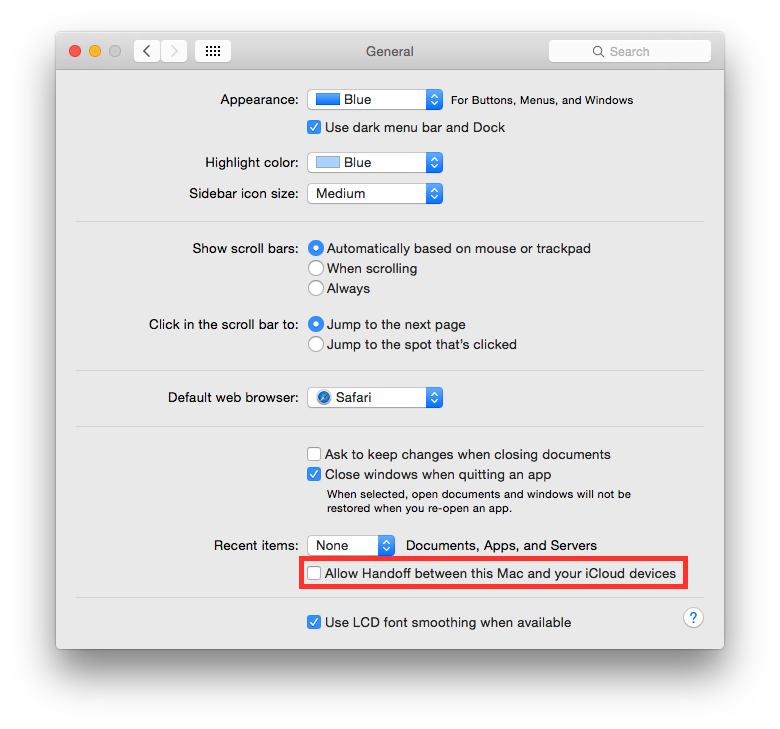
Disable password hints¶
Passwords hints are supposed to help an user to remember his password but could also help attackers. It is suggested to disable password hints, go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Users & Groups ⇒ Login Options
Un-check “Show password hints”.
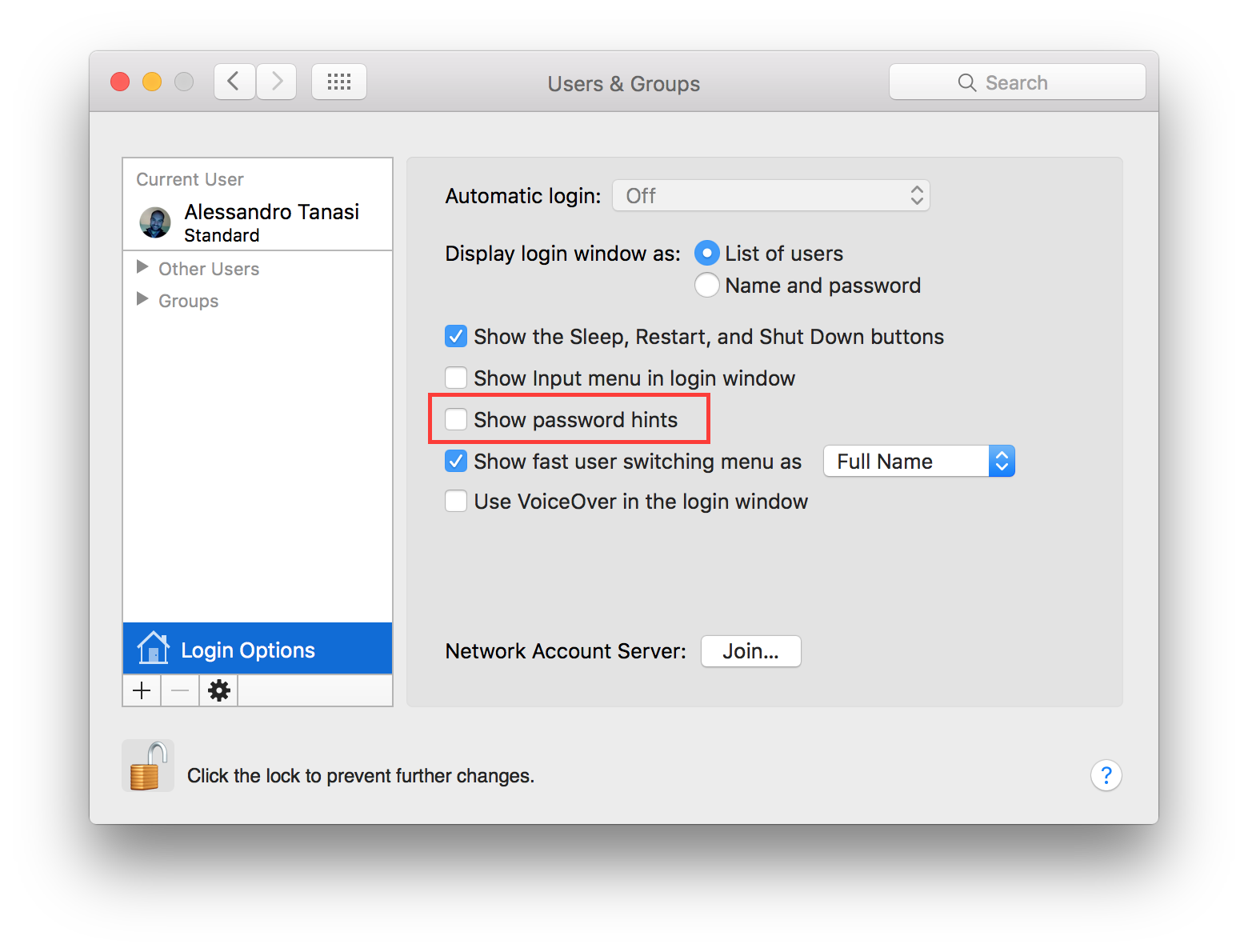
Disable recent items¶
Recent items are used to track your latest activity, it is also a feature used in forensics investigation to create the user activity timeline. It is suggested to not track last recently used items. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ General
Set “Recent items” to “None”.
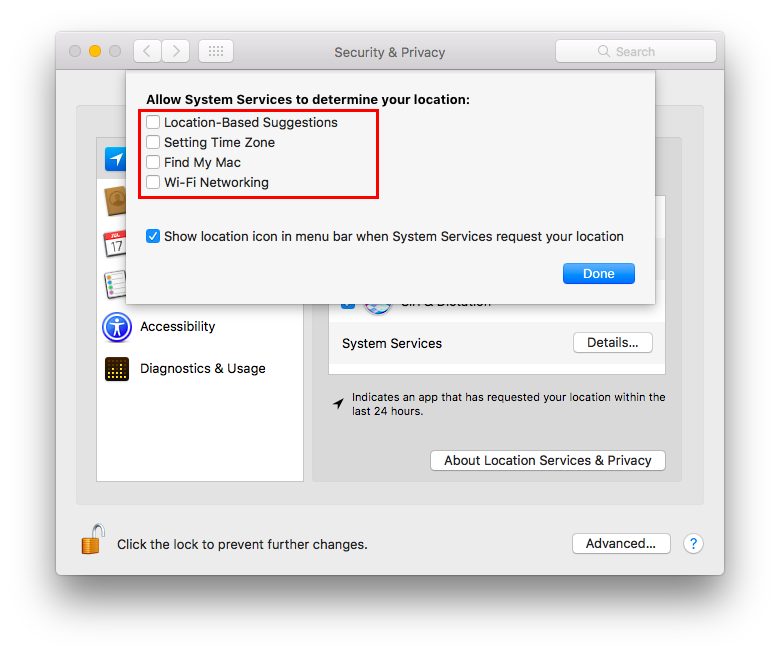
Disable Localization Services¶
By default Spotlight is allowed to use localization services to help you offering localized results. Due to his implementation it needs to send your position to a remote service. It is suggested to disable this behavior. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ Privacy ⇒ Location Services
Select “System Services” and click “Details…”. It is suggested to disable localization for all services, if not needed.
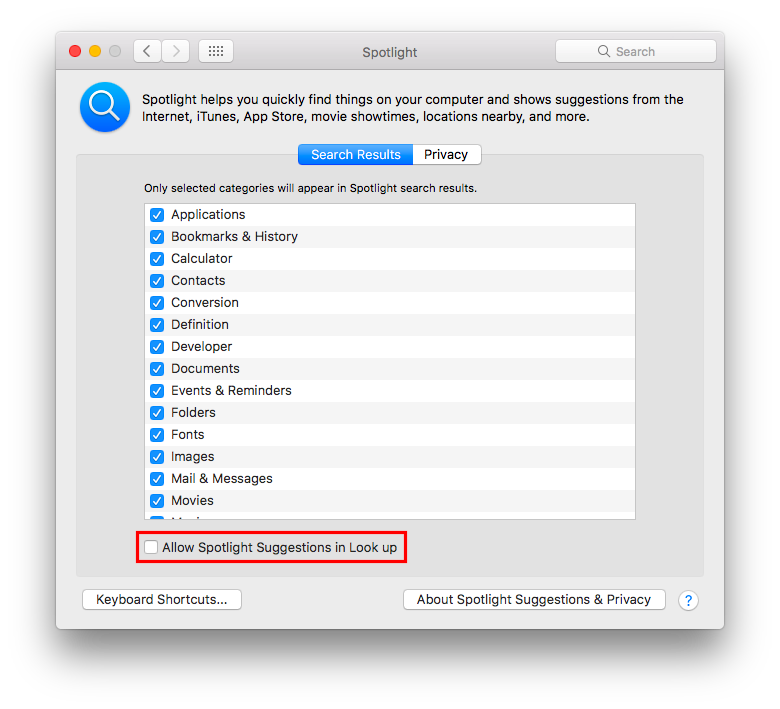
Disable Spotlight Suggestions¶
By default Spotlight shows suggestions from the Internet, it sends your search to Apple services and provides results back. It is suggested to use Spotlight only locally to prevent leaking your search. To disable Spotlight Suggestions go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Spotlight
Un-check “Allow Spotlight Suggestions in Spotlight and Look Up”.
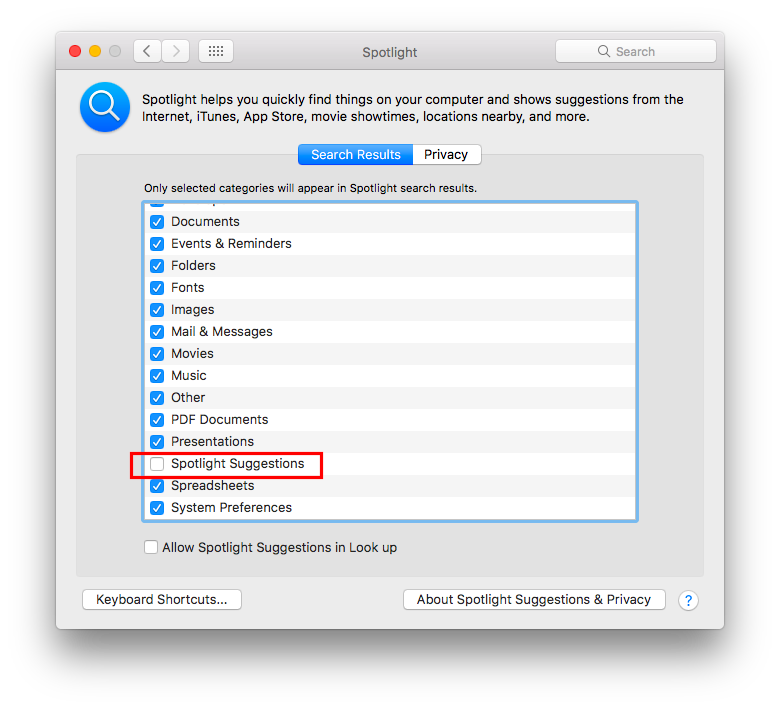
It is suggested to disable Spotlight Suggestions to avoid leaking your search to online services used for suggestions, go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Spotlight
Un-check “Spotlight Suggestions” from the list of results categories.
Enable FileVault¶
It is suggested to enable FileVault to enable full disk encryption on your device. It should be already enabled by default. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ FileVault
Enable FileVault.
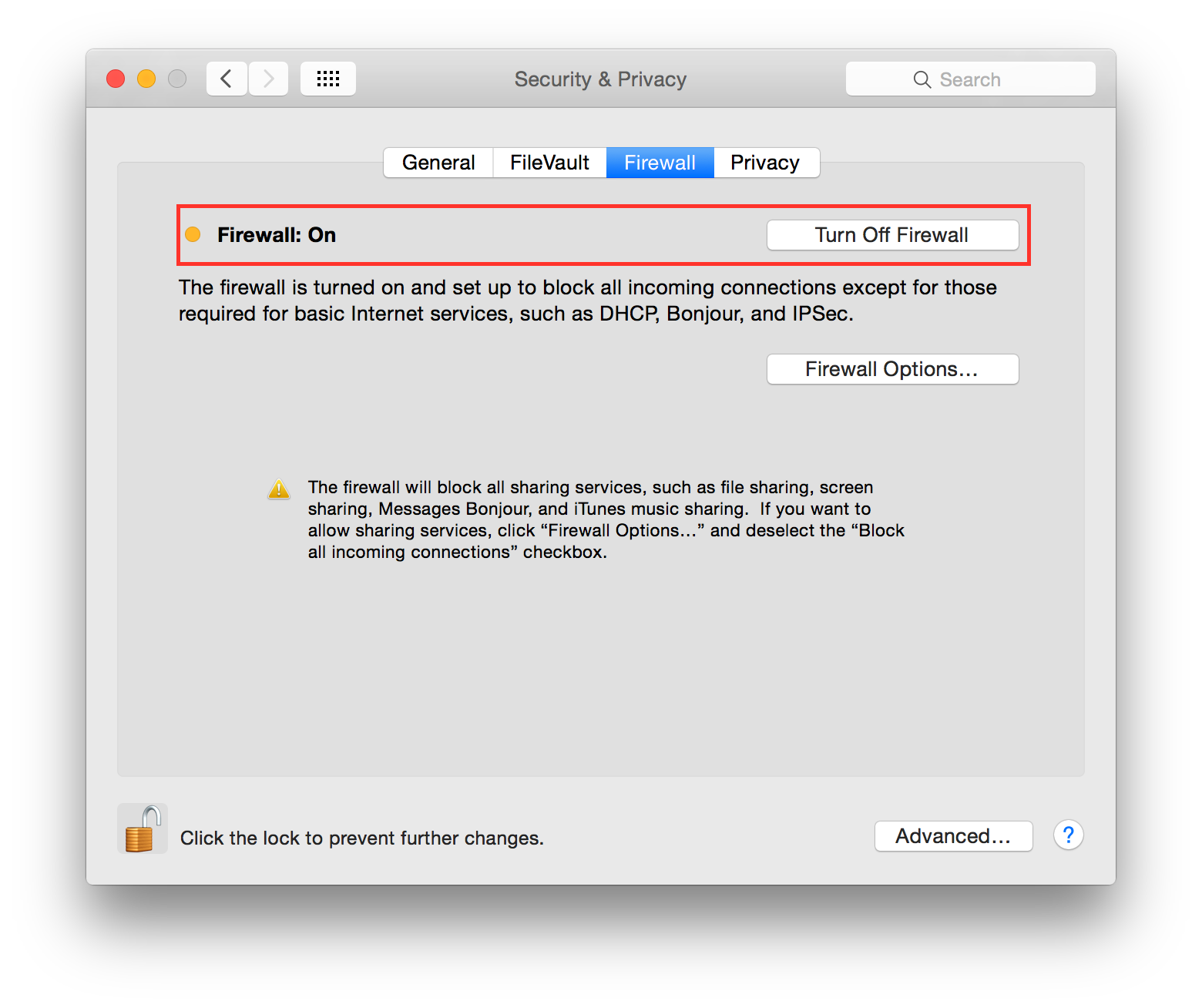
Enable Firewall¶
It is suggested to enable the Firewall and have it always running. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ Firewall
Click on “Turn On Firewall”.
Now click on “Firewall options”, a new panel will appear. Click on “Block all incoming connections”.
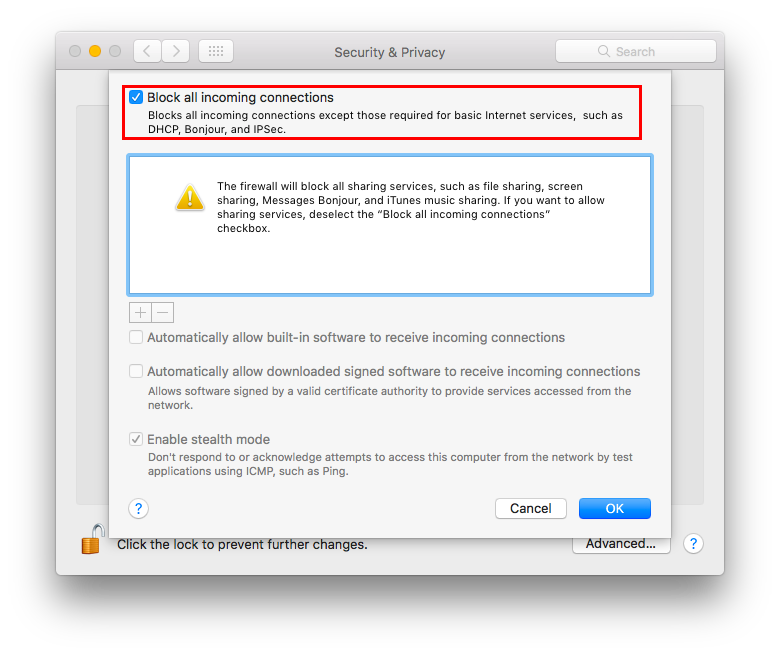
Using “Block all incoming connections” will block all incoming connections to your host. This will block also all sharing services, such as file sharing, screen sharing, Messages Bonjour, iTunes music sharing and other features. If your host is providing any kind of service, this option is not suggested; you should disable it.
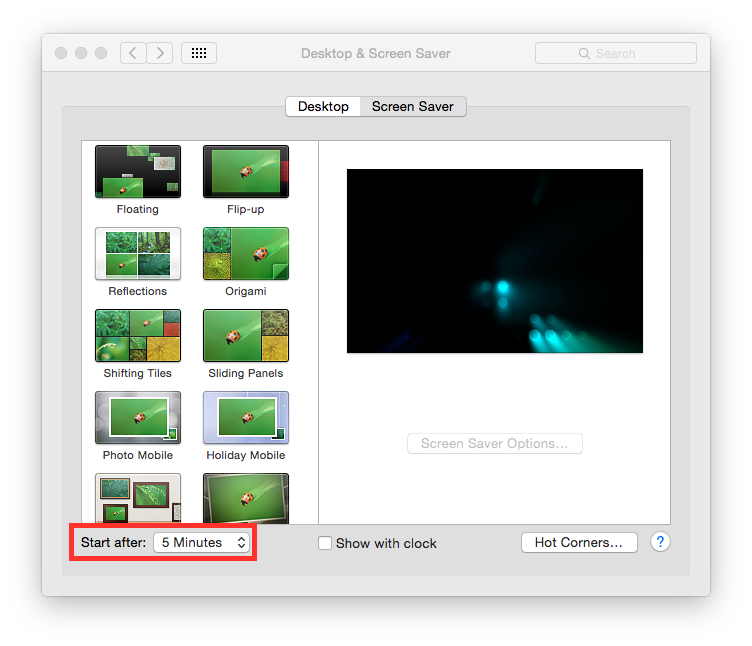
Enable screen saver¶
It is suggested to enable the screen saver to automatically lock your screen after a while. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Desktop & Screen Saver ⇒ Screen Saver
Set “Start after” to “5 Minutes”.
Empty trash securely¶
When you delete a file, OS X only deletes the index entry for the file, which tells the system the file’s contents are free to be overwritten; however, the data still remains and may be recovered using a forensics software. It is a good practice to always empty your trash securely. Your data will be securely wiped from disk in an irreversible way. In the previous OS X releases there was an option to enable safe delete, Apple has removed this feature in OS X El Capitan. However, you can use command line tools.
You can use the rm command from Terminal to delete files with the -P option, as stated in man rm this option is used to:
Overwrite regular files before deleting them. Files are overwritten three times, first with the byte pattern 0xff, then 0x00, and then 0xff again, before they are deleted.
For example if you what to delete test.pdf you should open Terminal and use:
$ rm -P test.pdf
Erase free space¶
In some cases, you might want to run an overwrite task on the free space of a given drive. You can use the diskutil command line utility, open Terminal and use:
diskutil secureErase freespace LEVEL /Volumes/DRIVE_NAME
In this command, change LEVEL to a number of 0 through 4, the available options are:
- 0 is a single-pass of zeros
- 1 is a single-pass of random numbers
- 2 is a 7-pass erase
- 3 is a 35-pass erase
- 4 is a 3-pass erase
Change DRIVE_NAME to the name of the mount point.
Homebrew hardening¶
Homebrew is a quite common third party tool in OS X systems.
It is suggested to disable anonymous statics collections adding the following variable to your .bash_profile or .profile (or your shell configuration) file:
export HOMEBREW_NO_ANALYTICS=1
It is suggested to disable automatic updates to keep in control of brew updates, add the following to your .bash_profile or .profile (or your shell configuration) file:
export HOMEBREW_NO_AUTO_UPDATE=1
It is suggested to configure brew to do not leak your GitHub username. When checking out a public repository, by default, your username is always sent. Add the following to your .bash_profile or .profile (or your shell configuration) file:
export HOMEBREW_NO_GITHUB_API=1
Is is suggested to configure brew to avoid protocol downgrades from HTTPS to HTTP via redirect. Add the following to your .bash_profile or .profile (or your shell configuration) file:
export HOMEBREW_NO_INSECURE_REDIRECT=1
Power off memory during standy¶
By default during stand-by memeory are kept powered on, this is prone to forensics acquisition of your memory. As stated in man pmset:
hibernatemode supports values of 0, 3, or 25. Whether or not a hiberna- tion image gets written is also dependent on the values of standby and autopoweroff
For example, on desktops that support standby a hibernation image will be written after the specified standbydelay time. To disable hibernation images completely, ensure hibernatemode standby and autopoweroff are all set to 0.
hibernatemode = 0 by default on desktops. The system will not back memory up to persistent storage. The system must wake from the contents of mem- ory; the system will lose context on power loss. This is, historically, plain old sleep.
hibernatemode = 3 by default on portables. The system will store a copy of memory to persistent storage (the disk), and will power memory during sleep. The system will wake from memory, unless a power loss forces it to restore from hibernate image.
hibernatemode = 25 is only settable via pmset. The system will store a copy of memory to persistent storage (the disk), and will remove power to memory. The system will restore from disk image. If you want “hiberna- tion” - slower sleeps, slower wakes, and better battery life, you should use this setting.
It is suggested to power off memory at stand-by with the following command:
sudo pmset hibernatemode 25
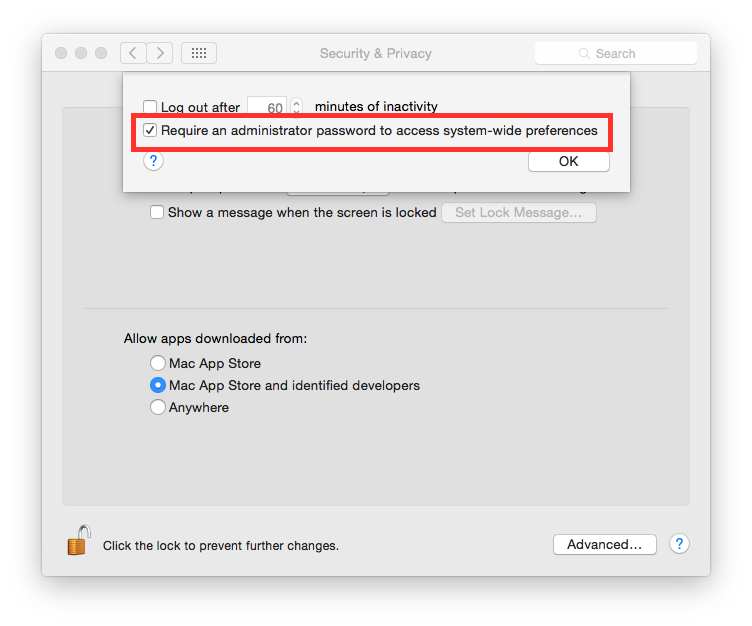
Require an administration password¶
Always require an administration password to access system settings. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ Advanced
Check “Require an administrator password to access system-wide preferences”.
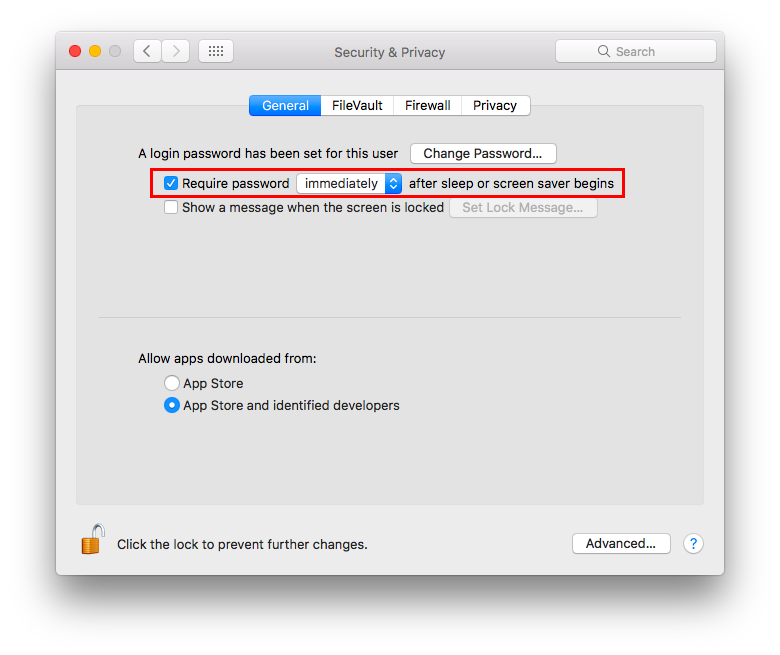
Require password to un-lock¶
Requires password to un-lock from sleep or screen saver. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ General
Set “Require password immediately after sleep or screen saver begins”.
Save to Disk by Default¶
Many applications bundled in OS X, i.e. Text, save by default new documents to iCloud. It is suggested to set default save target to be a local disk, not iCloud with the following command, open Terminal and type:
defaults write NSGlobalDomain NSDocumentSaveNewDocumentsToCloud -bool false
Set a Firmware Password¶
Enabling an optional firmware password offers an increased level of protection. A firmware password is set on the actual Mac logicboards firmware, it is an EFI password which prevents your Mac from being booted from an external boot volume, single user mode, or target disk mode, and it also prevents resetting of PRAM and the ability to boot into Safe Mode. Years ago firmware passwords could be easily bypassed by removing memory. These days Mac’s firmware password isn’t easily reset. Apple only suggests to bring your Mac in to an authorized Apple Service Provider and have them do it there.
It is suggested to set a firmware password:
- Power off your Mac and turn it on.
- Activate Recovery Mode (holding down the Command and R keys at boot).
- After a while OS X Utilities will appear.
- Click on the Utilities menu from the menu bar.
- Select Firmware Password Utility.
- Click on ‘Turn On Firmware Password’ and follow the wizard.
- When done, restart your Mac.
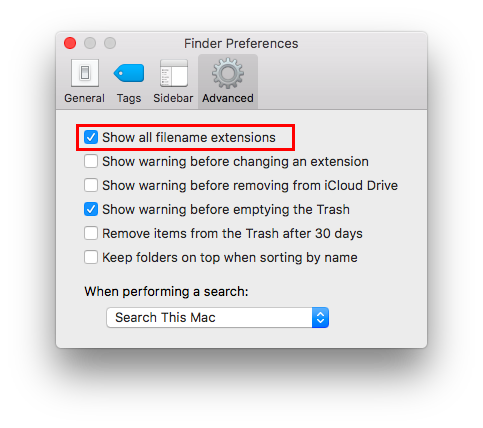
Show all filename extensions¶
It is a good practice to always show file names extensions. Start Finder app. Go to:
Preferences ⇒ Advanced
Check “Show all filename extensions”.
Show when localization is used¶
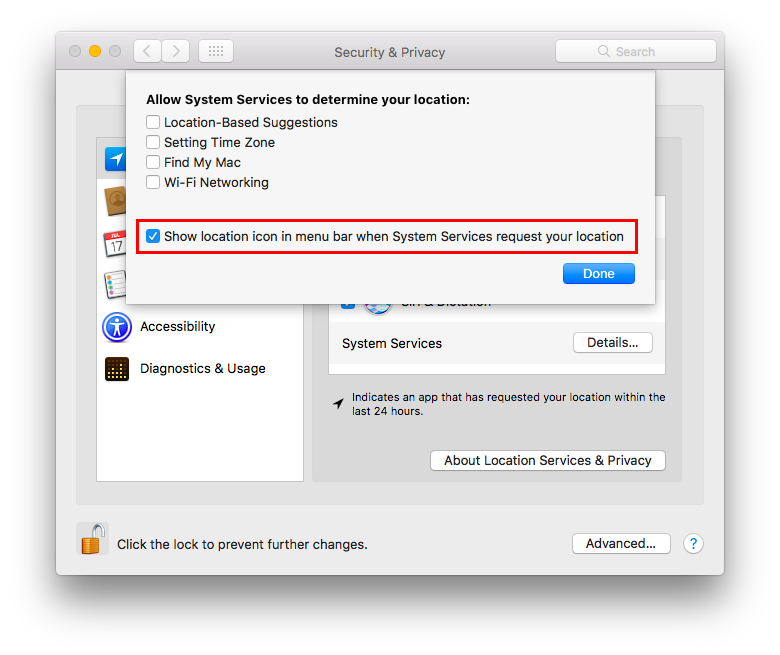
System services could ask to use localization data. It is suggested to show location icon when localization data are requested. Go to:
System Preferences ⇒ Security & Privacy ⇒ Privacy ⇒ Location Services
Select “System Services” and click “Details…”. Check “Show location icon in the menu bar when System Services request your location”.
Users privilege separation¶
It is suggested to use different accounts for administration and normal use. Create an account with admin privileges for special tasks and maintenance and a regular user for your normal use. Don’t use the same password for both.